What is Google Tag Manager (GTM)?
Google Tag Manager is a free tool that permits you to manage and deploy advertising tags on your website or mobile app without having to change the code.
What Is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a tag management system (TMS) that permits users to simply add and edit snippets of custom or templated code–called tags–to a website. Tags can add analytics tracking, manage promotion pixels or make additional site functionality. GTM contains dozens of predefined tag templates needing no custom coding.
Components of tags & GTM
On the surface, tags and tag managers are attractive frank. But before you can start at work with them, there are a few key concepts you’ll prerequisites to distinguish about.
Containers
When you start working with GTM, the initial thing you’ll need to do is generate a container. A container basically “holds” all the tabs for your site.
After making a new container, GTM stretches you some code to add your site. This is your container program and it will essential to be added to the source program so it shows on each page of your site. Once you have completed, you’ll be able to add, manage, disable, or eliminate your tags as needed through GTM.
Triggers
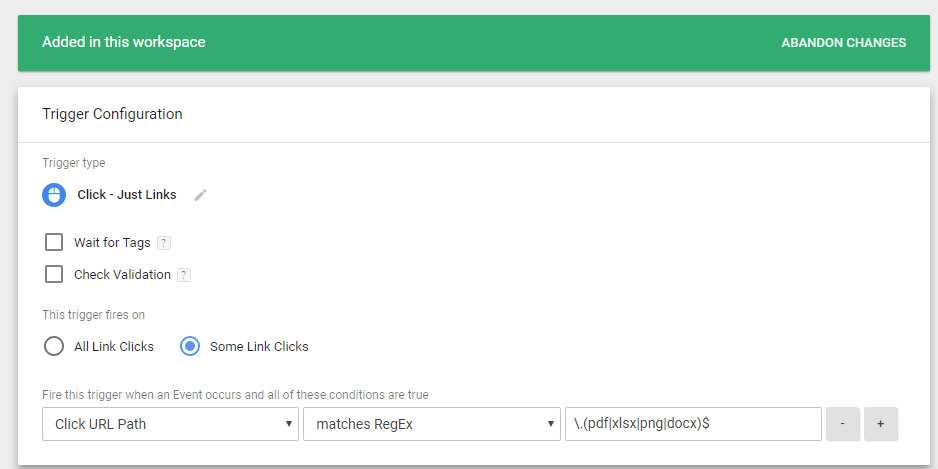
Each tag on a site wants to serve a specific resolution. Maybe you want to have a tag lead information when someone downloads a file, when an outbound link is connected, or when a method is submitted. These sorts of actions are known as triggers and all tags essential to have at least one trigger allotted to it. When you go to organize a trigger in GTM, you’ll be specified a long list of types of triggers to select from. These are events. Once you pick an event, you’ll be able to establish your filter.
Variables & constants
While tags depend on triggers, triggers depend on variables. Variables hold the value of a trigger wants to estimate to know whether or not it would fire. The tag relates the worth of the variable to the value defined in the trigger and if the variable sees the conditions of the trigger, the tag will fire.
Data layers
A data layer is a JavaScript object which preserves the information tags that need to be isolated from the rest of your site’s code. Since tabs don’t have to occupy time searching over the HTML to find the info they need, this is one more way GTM can aid improve site speed. Instead, all they’re viewing for can be found in one place and it’s eagerly available when the page loads.
The Pros and Cons of GTM
Reduces Reliance on Web Development
By far, the main benefit to Google Tag Manager is that it makes it easier for marketers to implement tags deprived of having to rely on web developers to fix it for them. Developers are typically busy with other high-priority developments, so tagging frequently ends up on the back burner. But since Google Tag Manager supports you avoid moving the source code, marketers can speedily add and make variations to tags on their own.
Still Requires Some Technical Implementation
Even though GTM aids to reduce the dependence on developers, it doesn’t eliminate it. While GTM has a lot of tag patterns to choose from which are calm enough for a non-developer to work with, more compound modified tags will probably require the help of somebody who realizes coding. If you have existing tags that were automatically added to your site’s source code, those will need to be detached first so that you don’t end up with replica data.
Most Businesses Can Benefit for Using It
Businesses of any size can benefit from GTM. Since GTM types it so much easier to improve and edit tags shorn of a developer, it’s great for smaller businesses that might have partial access to technical provision. And since sites for enterprise-level businesses can simply use lots of tags, GTM makes it calmer to manage them all and expands site speed by helping them load more proficiently.
Tags Can Slow Down Site Speed If Fired Synchronously
One problem with traditional following tags is that if they fire synchronously, they can slow down site haste. When tags fire synchronously, one tag being deliberate to load slows down all the other tags that are to come on it. And the lengthier site takes to load, the more likely it is that persons will leave without changing. But tags formed in GTM load asynchronously by defaulting, meaning to each tag can fire anytime it’s ready to.
Used for AMP Sites and Mobile Apps
You’re not even restricted to just using GTM with usual websites. GTM can also be cast-off to manage tags for AMP places and mobile apps. In the case of mobile apps, GTM can be a vast help since it allows you to add and edit your tags without having any problem in an updated version of your app, which users might not be fast to download.
Working with GTM
Creating a Tag
When you generate or select a container, the initial thing you’ll see is the GTM dashboard. We’ll finally get around to chatting about nearly everything you see here, but let’s start by creating a tag. Click “Add a New Tag” to exposed up a window where you’ll be clever to name and configure your tag.
Previewing, Debugging, and Publishing Tags
GTM’s “Preview & Debug” method lets your exam tags before publication so that you can make sure everything is employed correctly and that you won’t have any mistakes throwing off your data. To enter “Preview & Debug,” click the “Preview” key in the upper right corner of the GTM dashboard and you’ll see an orange banner informing you that you are now in “Preview” mode.
Even later a tag has been published, Google still creates it easy to go back and checked to make sure there aren’t any difficulties. Google Tag Assistant is an allowed Chrome extension and after it’s installed, you can visit any page on your site and it will show you if your tags are working properly or if any developments could be made.
Workspaces, Workspace Changes, and Activity History
If you have many people working on a tagging project at a similar time, workspaces can help make life a slight easier.
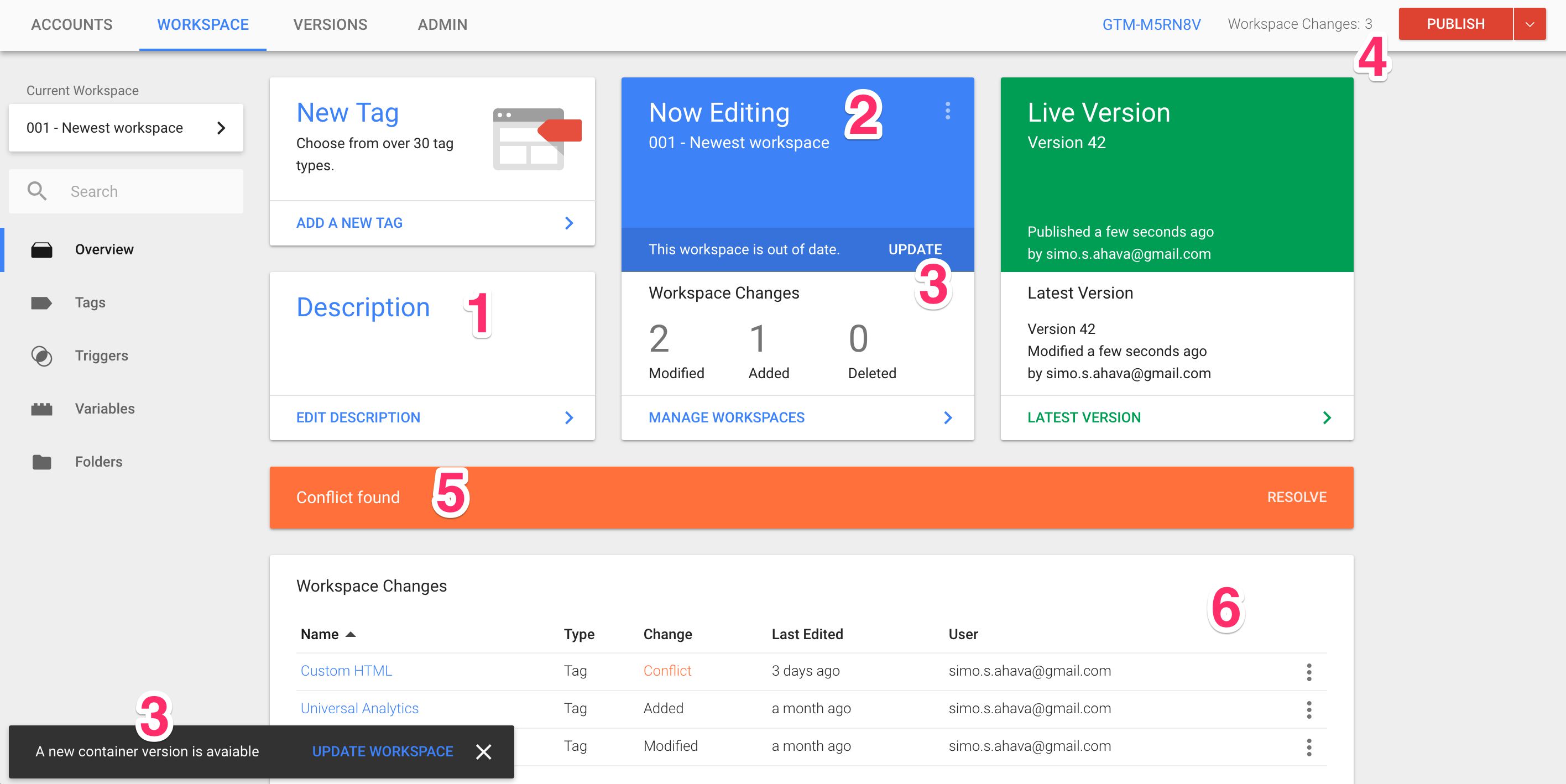
In older types of GTM, all controls had to be complete in a common container draft. If one person or team completes adding tags earlier another person/team, they couldn’t publish their new tags without also publishing the other team’s tags-in-progress. But with workspaces, many users can work on tagging at the equal time without interfering with each other’s work.
Reasons Why Google Tag Manager Is Special
Free
Not to concern, it’s together free and awesome! Google Tag Manager consumes a multitude of robust structures, with usability, accounts and user characters, tag firing rules, and maintained tags
Do It Yourself
Addition the container tag once, make variation whenever you need without much bother, and voilà! With the presented debugging tools and preview mode, you can be definite of what you’re doing formerly you publish it.
Features with Google Analytics
Google Tag Manager types it easier to implement nearly of the more difficult Google Analytics structures, such as User ID tracking. User ID chasing gives you the capability to measure real customers instead of devices. Tag Manager also supports common tasks in Google Analytics, such as Cross-Domain Tracking, Custom Dimensions, for many sites that are followed together in Google Analytics, and Enhanced Ecommerce that needs collaboration with developers.
Easily Track More Things
With so many great properties available on the web it’s easier than ever to track effects like YouTube videos on your site, AJAX form submissions or print tracking.
Security
Google Tag Manager has all of the safety features of your necessity. One awesome feature is two-factor verification that needs both your normal PIN and then a numeric code that you obtain via a text voice call, message, or mobile app. You are also able to switch the access by conceding dissimilar levels of approval at both the version and container levels.









